How do you design an irrigation system?
Last week we dealt with the design of the project and you can find it in this article “THE IRRIGATION SYSTEM FOR THE GARDEN: THE PROJECT“.
In today’s article, however, we will find out how to build our irrigation system by answering some questions, including:
What is needed to build a garden irrigation system? How do we make it and how much does it cost to build or have an irrigation system built?
How to build a garden irrigation system
Before us we have the drawing of the irrigation system that we designed with great pride or delivered by the professional.
The design of our plant is made to scale, by hand or aided by the computer. And now?
What do you need to buy to build an irrigation system?
The list of materials to be purchased is net of the instrumentation necessary for the construction which includes both machines and material for cutting, joining, connecting, etc.
The elements to create the system for our garden are:
- a control unit (one or more zones);
- one or more coils of 32 (mm) diameter high-density tubing;
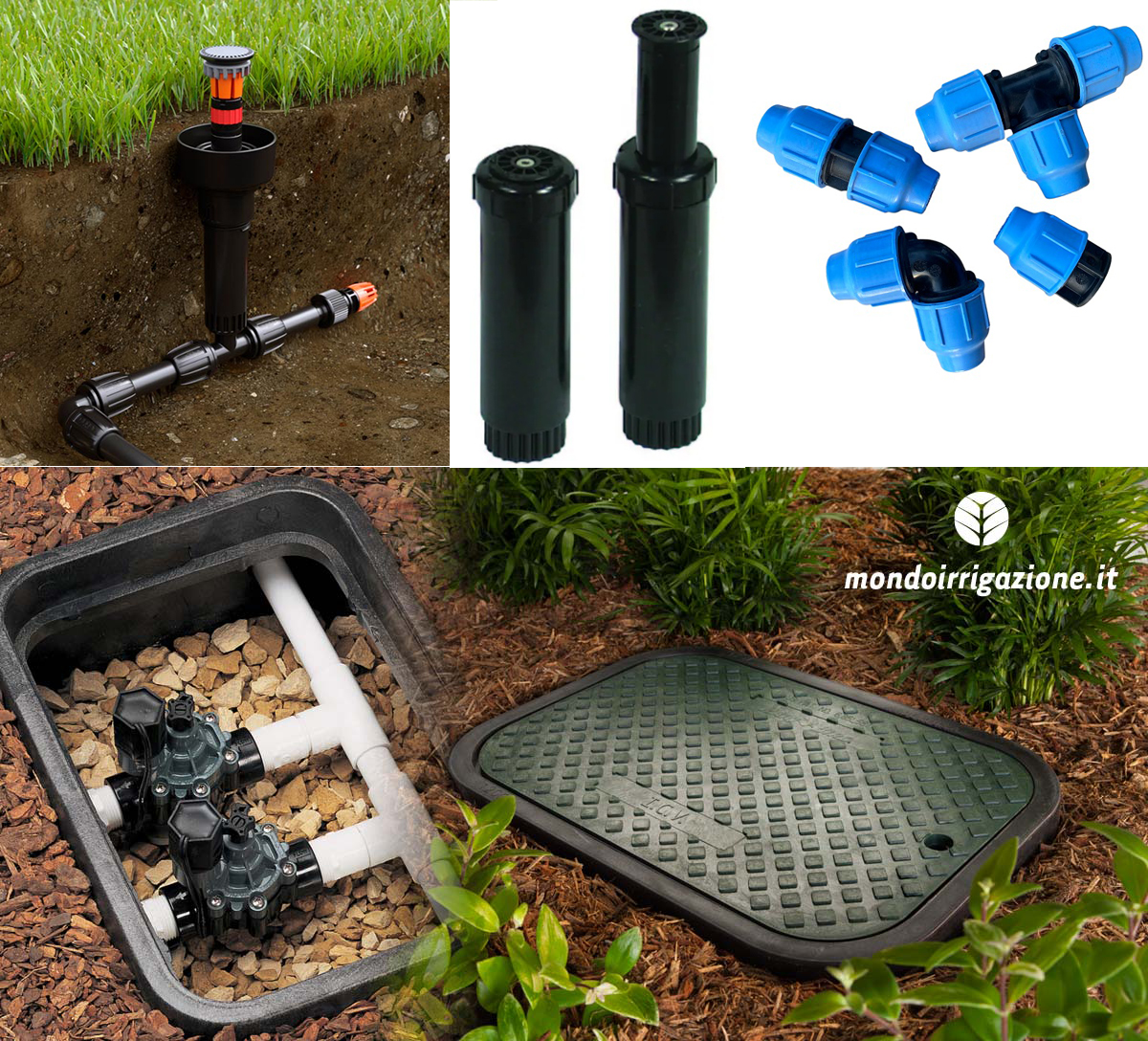
- one or more solenoid valves if divided into zones (one per zone);
- at least one well for the solenoid valves;
- static sprinklers (if needed) + 10;
- dynamic sprinklers (if necessary) + 10;
- one or more dripline coils;
- the rain sensor.
If you really decide to do this job on your own, ask the person who will sell you the material for advice, but be aware that you will incur costs for renting machinery and the risk of procedural errors – if not physical damage – which may not only be encountered by those who know the job .
The first step for the construction of the irrigation system: the excavation
The excavation for the placement of the pipes must be approximately 40 cm deep and 20 wide. The length corresponds to the entire system circuit.
It can be done, for private gardens, in two ways: by hand or with a machine.
We don’t have to tell you that digging by hand is long and heavy to perform, however it is doable and very zen – the time spent in the garden making physical efforts with a clear mind, if used well, allows us to solve or at least address unheard questions of our life.
The machine, on the other hand, tackles the excavation faster and with less effort because it was built specifically for this purpose.
Its name is CATENARIA and it can be manual or self-propelled, which can be rented if necessary.
What is the irrigation system control unit and what is it for?
The control unit allows you to set, in the simplest situations, the number of days a week you want to water and the number of minutes of irrigation.
If the system is divided into several zones (if you haven’t done so yet, read “THE GARDEN IRRIGATION SYSTEM: THE PROJECT“ to see some examples of a garden divided into zones) the control unit will be a little more complex and will also allow you to manage the switching on and off sequence of the various zones. The operation of this type of control unit requires that the waterings go in sequence.
For example, if we have three zones, the one we set as number one will start first. Once the irrigation minutes in zone one are over, the solenoid valve will close that path in that pipe and open the passage to the zone two pipe for the number of minutes that we will set which may be different from the irrigation minutes in the first zone if the sprinklers are different from first or are dripline. Finally, once the irrigation minutes in the second zone are finished, the control unit will order the solenoid valve to close the connection with the pipe in the second zone and it will switch to the third for the set number of minutes. If it is a dripline, the irrigation time will be much longer than that of the others, as only one drop will come out at a time.
Pipes and dripline for irrigation systems: What they are and what is the difference
We mentioned, in the previous article, the pipes and the dripline. Let’s study them better.
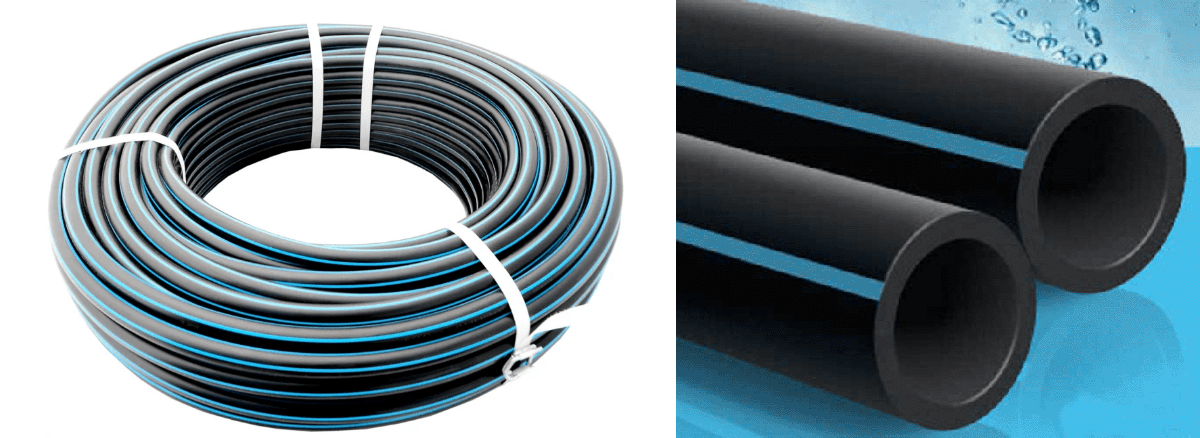
The underground irrigation pipes are made of high-density polyethylene and are resistant to pressurized fluids. They are often black with a blue stripe and are brought to site in large skeins which will then be unrolled on the ground and cut to the required lengths at the fittings and solenoid valve.
These pipes manage static and dynamic sprinklers that you already know what they are because we talked about them in the article mentioned at the beginning, but we will talk more about them below.
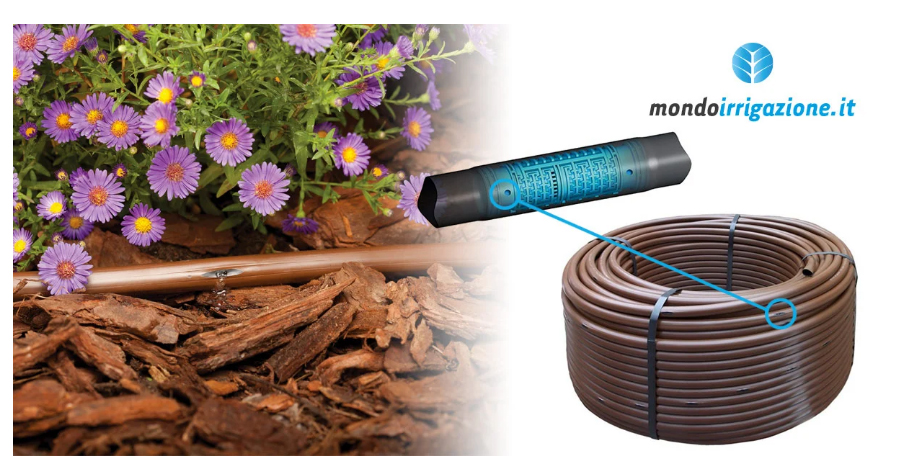
The dripline, on the other hand, is a black or brown pipe that contains sprinklers and holes along its length and that throws drops out of these holes, without making a spray that rises.
It is used to be placed on the ground under the flower beds to prevent the flowers from getting wet and under the hedges.
As we mentioned above, this type of irrigation throws out much less water than a popup sprinkler must be in a separate area and passed around each plant several times.
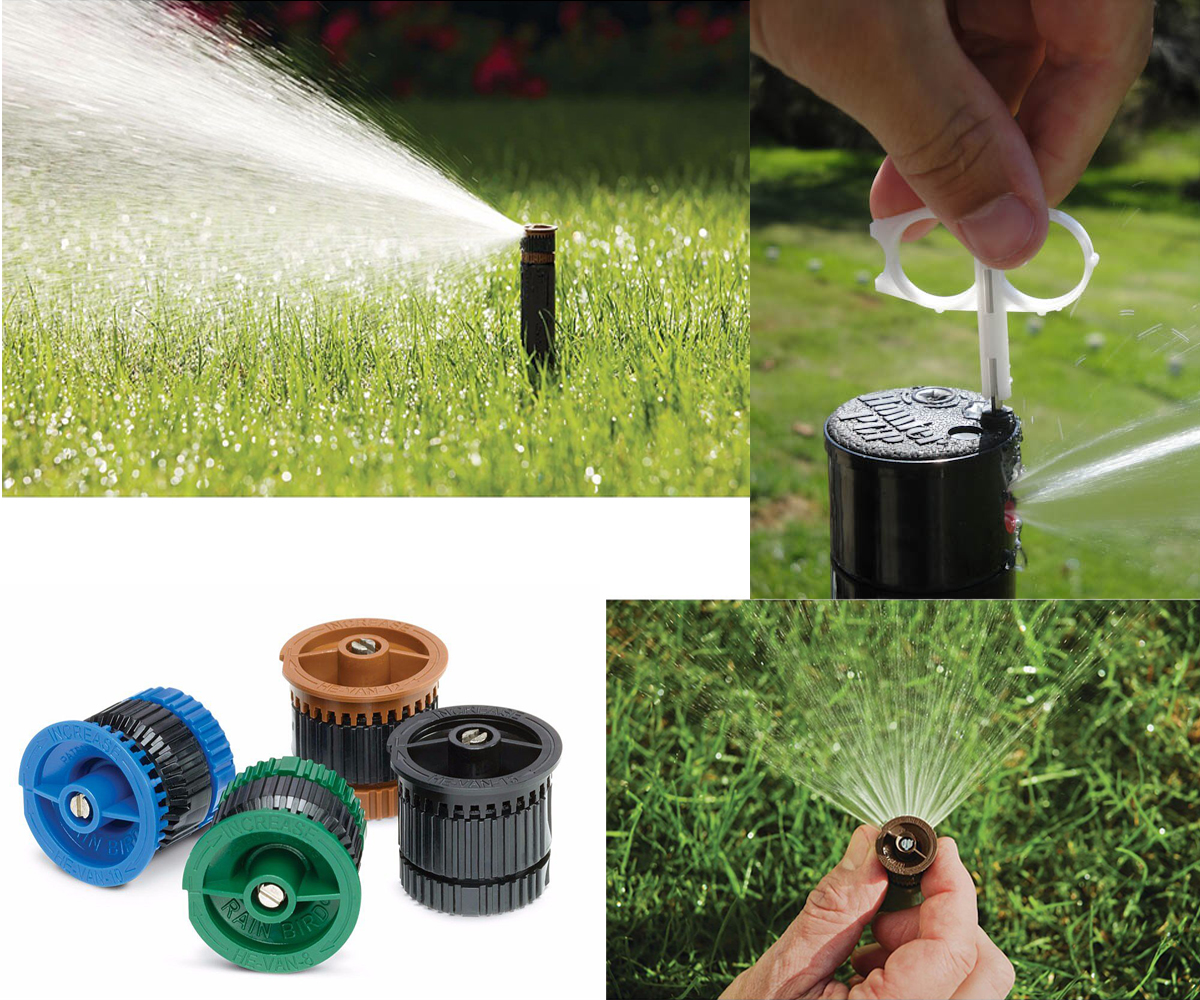
What are Static and Dynamic Popup Sprinklers? What elements are they composed of?
Popup sprinklers come in two types: static and dynamic. They are both made up of a fixed body buried flush with the ground and a part which, when at rest, is housed in the buried body and, under the pressure of the water when turned on, are pushed upwards.
Where are sprinkler nozzles located? What are they for?
On the top of the sprinkler is a replaceable part which is the nozzle. The nozzle is what decides where the water goes. It can be fixed or adjustable and each company has its own.
As you can see on the nozzle there are some things written and they are of different colors. This will help you remember what characteristics it has like firmness, range, etc. For example, the throw is the arc of water that covers that sprinkler.
The range: How it works and how to manage it
The drawing above just shows how more water goes at the end of the stream and the closer you get to the sprinkler the less water is dispensed. For this reason the sprinklers must always be placed facing each other.
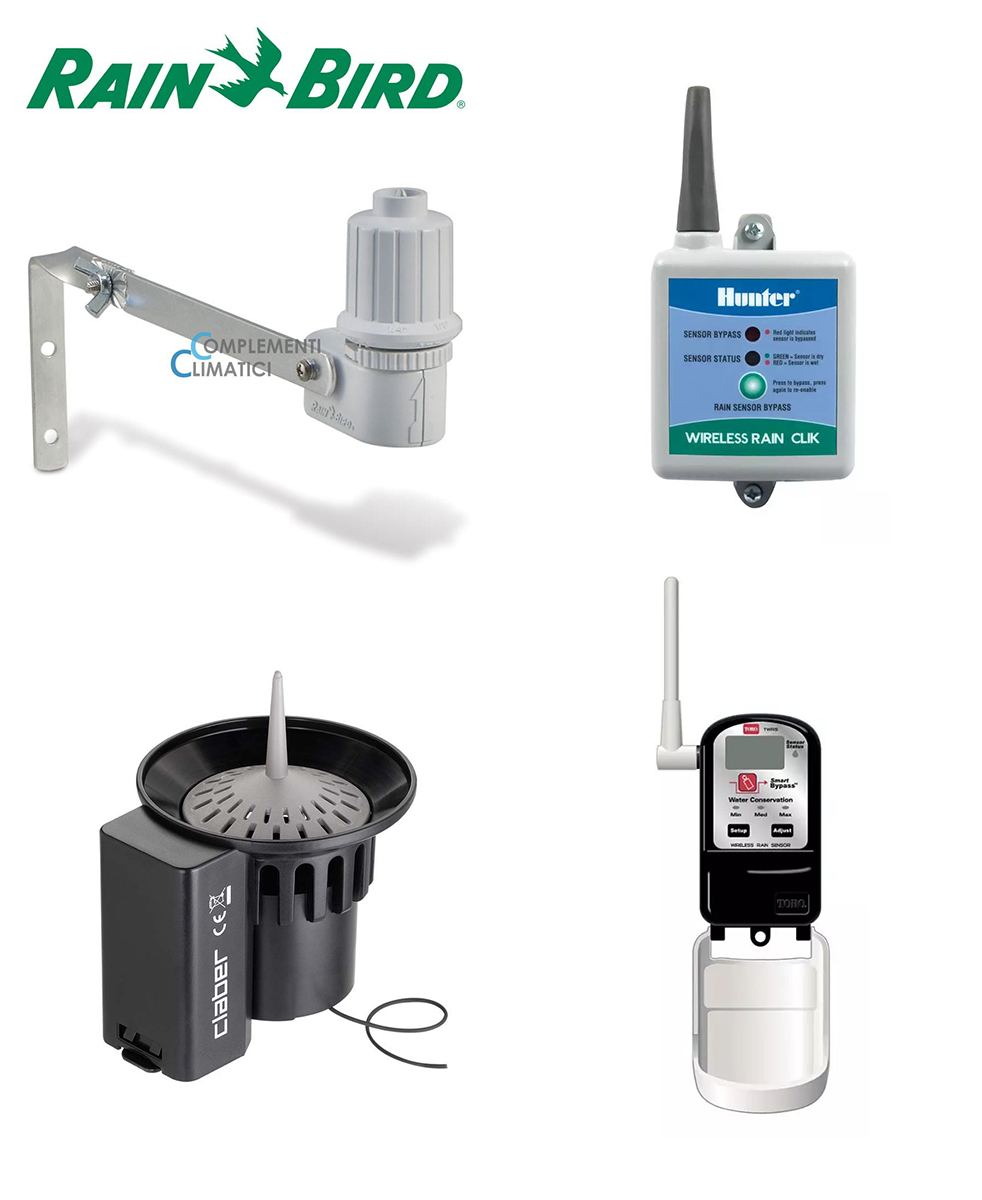
What is the rain sensor and what role does it play in our irrigation system
The rain sensor is important. This element must be positioned at the mercy of the elements and when it rains it notifies the control unit not to start. Don’t skimp on this economically because otherwise it works badly, it doesn’t do its job, you use more than the necessary water and you will have spent money unnecessarily.
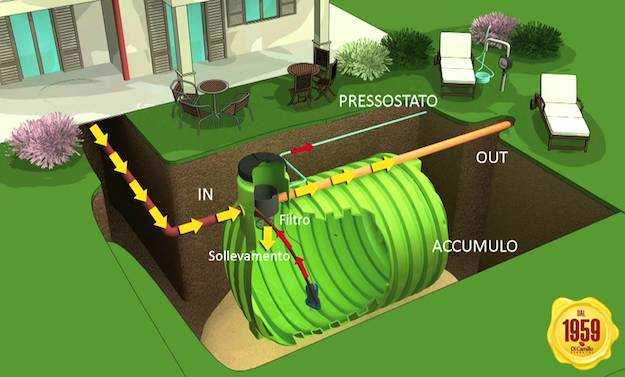
Additional elements for the irrigation system: The cistern and the well
In case you want to convey rainwater or from a nearby canal, you can install an underground (or not) cistern from which you will take water for irrigation. If you bury it you will need a submersible pump that lifts the water to be used and gives the necessary pressure.
The cost of this work, including purchase, transport, excavation, burial and preparation of the tank connections vary according to the size of the tank. If I were you I would calculate at least 3,000 euros, up to about 8,000.
For the well there are clearly no installation costs, but a submersible pump will still be needed for the reasons mentioned above and also in this case we recommend inserting a tap just in case.

Here, as I promised you in the previous article, is the link where you can find the description of how to divide the garden into irrigation zones on mondo irrigazione.it:
THE WORLD OF GARDEN TIPS
Be careful when cutting grass. Buy more sprinklers than you need, at least 10 x type and memorize or remind the gardener the position of the sprinklers so that you don’t walk over them with the lawnmower because it could break them.
Now on horseback! Work awaits us! Our new wonderful outdoor space is about to be born!
GOOD WORK and…if you have any questions or want to send photos of your finished work, write to info@ilmondodelgiardino.com
Fonti delle immagini: thanks from Pixabay for the pickaxe Carola68, for the spade in the foreground Anders Majlvang, for the well with tap Volker Lekies; for the Irrigated forest Couleur; for the catenaries uprent.it, edilsiena.it, noleggiando.com, sborgia.com; for the control units rain.it and ilmiogiardino.net; for the polyethylene pipes puntoirrigazione.it and tecnoresine.net; for the dripline, mondoirrigazione.it; for sprinklers faidateingiardino.com, leroymerlin.it and rainbird.com; for fittings iuzzolinifortunato.com; for the well mondoirrigazione.it; for nozzles rainbird.com and hunterindustries.com; for the scheme of the flow mondoirrigazione.it; for the rain sensors, complementiclimatici.it, pratoerboso.com, irrigazioneonline.com and Claber.com; for the landfill scheme of the cistern ideegreen.it.